Banter 61 will be conducted by Zoom on Saturday, February 27th at 1030 MST.
Link to meeting (click here)
Meeting ID: 898 2676 8563
Pass: Banter61
_____________________________
FROM ISAAC:
Below is an OED definition of positivism (in a Google Search):
This guy might be more of an interesting case study than a wise philosopher, but I basically agree with him:
Writing this reminds me just how much I am not a writer, it seems so difficult to put words down and have them mean what you want them to. I guess it’s best not to want any control over meaning.
The answer to the discussion topic I think is no. I am currently tired of being in the human species when I see how we humans around the world just keep being horrible to each other and to the earth. Nothing seems to change.
I could lean the other way though...yes, we do change. We are very adaptable with our large brains and can learn new tricks. Our thoughts evolve and we see things in new ways as we grow and mature. In a sense, every time our mood changes dramatically we think differently. When you fell in love thoughts were bright, driven by joy and appreciation. when you were in bad mood or felt slighted thought patterns turn towards negativity.
And bright people work hard on changing toward betterment (Banter people for example.). Is that part of their permanent thought pattern? Research in neuroscience has shown that brain cells can change into different tasks. How interesting that a few people who developed blindness have learned echo location, making clicking noises. When studying those peoples’ brains with MRI they find that the occipital (visual cortex) lobe is what’s busy reading objects and direction from sound. This shows there is nothing intrinsic about a visual cortex neuron versus a pain sensing neuron versus a motor neuron. e.And people who study very hard day after day find new ways of thinking I believe. But it takes effort, repetition, and some kind of reward.reward seems important.
Really, I could go either way on this. We are all marvelous and we are all not marvelous.
_________________________________________________
FROM SABINE:
When I face my most entrenched neural pathways (often when I am stressed, too busy, or overstrained to do anything but be entrenched), or when I face the most regularly traveled neural pathways of my mother or a relationship/friendship I’m frustrated by, I will give one answer to this question. “No, our default settings and cognitive distortions will always rear up, take over again, and keep our dynamics somewhat fixed with others,” I might say.
But if I am outside walking on the sides of mountains a lot in calm, breath-aware manner, or reading poetry every day for a string of days (i.e. life is such that I am calm enough to be valuing reading poetry every day), or engaging in mindfulness/meditation/yoga that isn’t reserved for the mat but oozes out onto the rest of my day (I have accomplished this a few periods of life, though not presently), then I give wholly another answer to this question in a softer, softly amused voice. Something like this I might say then, “There are nearly infinite moments in the day stretching before me right now where I can opt to notice a lot of different things. Can I notice only my cognitive distortions or discomforts? Of course, some days that’s what I decide to do with my day, and it feels crummy. But, some days, I remember that I’m not locked into noticing only one set of things about myself or life, and those days, those moments anyhow, I tend to see in a much wider range of colors and sensations. Even my own suffering looks different when I recall I don’t have to view it only from one vantage point. It’s hard to remember this sometimes, very hard, but there are things one can do to make it easier to remember.”
I’ve always loved, at the beginning of a yoga class, to walk my students through noticing what their body is feeling (different sensations and where, pleasant and achy/sore/tense, how the breath feels moving the body, posture, weight, temperature), then refocusing to what their mind is doing (still, busy, over-efforting, quiet, listing, anticipating/predicting, sleepy, etc. until they can start to see the thoughts as if clouds floating across a sky), and then refocusing on how the emotional body/mind is (easy, peaceful, strained, sad, agitated, tired, a zinging nervous system, and so on). I think the more we don’t see our thoughts (or emotions) as synonymous with our entire being/body/self or state of existence, the more we can relegate the thoughts to being like clouds across a sky, not more important or loud than a foot that feels sore, or an eyebrow that feels very mellow and with no problems at all.
Therapy around recognising and then pushing back against cognitive distortions (including via Thought Records) can be okay for this changing/rewiring the mind in similar ways, but I think it is less effective (for me) as compared to straight up Buddhist (Pema Chodron) or MBSR (Jon Kabat Zinn) mindfulness practice, a life steeped in poetry, cultivating a wonder-filled child-mind, being actively nature-saturated, having a daily exercise-enriched life. These practices change my attitude, mindset, neural pathways I have access to, chemistry, level of belief in my thoughts, perceptions of what matters and what isn’t going to be helpful within my own body, and so on, much more than an hour of therapy a week, even years of it.
These three resources might slightly support further what I’m getting at about this:
- Jon Kabat-Zinn on mindfulness https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OcVmRUm3ok8
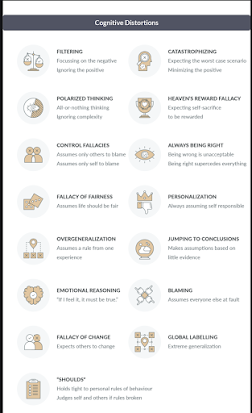
- List of 15 common cognitive distortions
(You can find this image & more details here: https://positivepsychology.com/cbt-cognitive-behavioral-therapy-techniques-worksheets/) - Thought record, blank (consider filling in once):
________________________________________
FROM PAM:
Here are a few prompts for conversation:
https://www.gardeningknowhow.com/garden-how-to/soil-fertilizers/antidepressant-microbes-soil.htm
https://www.neurologylive.com/view/neurobiology-forgiveness
________________________________________
FROM JARED:
I will admit my own ignorance on this topic because I do not see how positivism relates to changes in neural pathways. Perhaps if I better understood the origin of this topic, I would understand better.
At the risk—nay as proof—of my ignorance, I am sending a few thoughts.
Some psychologists call Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) the most effective method for treating “depression, anxiety disorders, alcohol and drug use problems, marital problems, eating disorders and severe mental illness.” https://www.apa.org/ptsd-guideline/patients-and-families/cognitive-behavioral. As that website explains, “CBT treatment usually involves efforts to change thinking patterns.” Twelve-step groups would relate it to the “tapes” that play in people’s heads. As I understand CBT, individuals learn thought patterns from our parents and friends when we are young, and some cognitive distortions spring to mind in related situations.
Often, those cognitive distortions take the form of “all-or-nothing” statements that undermine self-esteem. This website provides an example of all-or-nothing thinking in an interview in which the interviewee did not answer one question correctly. https://cogbtherapy.com/cbt-blog/cognitive-distortions-all-or-nothing-thinking. It proposed the subject could conceive of an all-or-nothing thought that “the interview went terribly.” Just as easily, the subject could stretch that into “I screw up every interview,” or “I never answer tough questions correctly,” or "Whenever something good is about to happen, I screw it up." None of those statements reflects the breadth of reality.
I see logical flaws in these thoughts. Logisticians would call those statements fallacies of hasty generalization: taking one example and extrapolating to a general principle. The psychological impacts arise from the general principle the thoughts establish: a feeling of worthiness or unworthiness. CBT helps people learn those logical fallacies in their own thoughts, and people can use those skills to combat the cognitive distortions toward a view that better approximates reality.
Separately, mindfulness can change thought patterns. Scientists call those potential changes neuroplasticity. https://www.forbes.com/sites/jeenacho/2016/12/27/the-science-behind-how-mindfulness-helps-you-to-break-negative-thought-patterns/?sh=4ef7066f4119. This article describes several changes in thought patterns that mindfulness can create. https://www.nature.com/articles/nrn3916
I met one woman who convincingly described the difference between the light side and the dark side of the Force as mindfulness.
Letting feelings of hate, anger, frustration, and disappointment control the individual leads an individual to the dark side. Letting those feelings wash over leads to the light side.



No comments:
Post a Comment